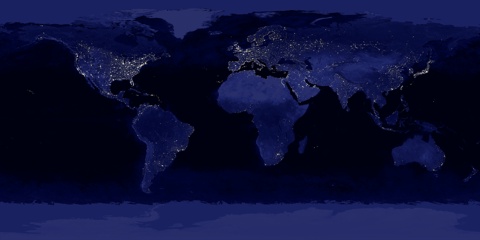
Fig.1. A photo mosaic of the Earth at night from space. Urbanized areas are clearly visible - Europe, North America, Japan (credit: NASA).

Fig.2. A night photo of Europe. Large European cites are clearly visible. The cites are seen from space at night as bright spots because outdoor lighting fixtures allow their light to escape above the horizontal plane (credit: NASA).
light pollution
The amount of artificial light used by mankind is growing rapidly since the mid 20th century. However significant majority of outdoor lighting fixtures is not correctly designed. As a result, significant portion of light emitted by those fixtures is directed outside the area which should be illuminated and thus is wasted, causing so-called light pollution. The wasted light being scattered by the atmosphere, causes increase of the night-sky brightness (nocturnal environment in general). The brightness of the night sky in highly urbanized areas is so high that only the brightest stars are visible. The Light Pollution Science and Technology Institute research showed that about 50% of the European Union population live in areas where the night sky is never darker than on nights close to full moon in uninhabited areas.
The problem of the light pollution is limited not only to the increase of the night-sky brightness and to resulting difficulty of astronomical observations. Effects of the problem influence many fields of life, unfortunately:
- [safety] Lamps shining into the eyes cause glare. This phenomenon results from excessive contrast between bright light source and darker surrounding areas. A human eye has difficulty in adjusting to differences in brightness because of the glare. This results in discomfort and in lower ability to see darker areas. Excessive, uneven and blinding road lightning can affect vision ability of drivers or pedestrians as well as distract their attention from obstacles, and contribute to accidents. Bad lighting is a particular impediment or even danger for people having some eye diseases. Poorly designed lighting close to airports may confuse pilots inducing hazard in the aviation.
- [ecology] The lack of darkness at nights influences many aspects of flora and fauna behaviour disturbing natural patterns of light and dark cycles (day, month, year). Light pollution can confuse animal navigation, alter interactions between different species, and influence animal physiology, foraging, reproduction, communication, and other critical behaviours.
- [human health] The light pollution has influence not only on animals but also on humans. Excessive artificial light at nights alters our natural day-night cycle. Health effects of light pollution may include: increased headache incidence, fatigue, medically defined stress, increase in anxiety, insomnia. Results of medical researches suggest that artificial light during the night can be a factor for breast cancer, due to suppression of the normal nocturnal production of melatonin hormone.
- [economy and ecology] Bad artificial lighting causes electric energy wastage and therefore public and private money misspent. The light which does not shine where and when it should or shining too excessively is as useless as a heat escaping from buildings through leaky windows and „warms” streets and parks. Electric energy wasted on the useless lightning must be produced by power plants. This means larger emission of pollutants, because currently most of the energy is generated by fossil fuel power stations. Paying for bad or/and needless lightning we „buy” extra air pollution then.
All above-mentioned subjects make the light pollution as serious problem as a chemical pollution of air, water and soil. Therefore an interest in solving this problem grows in the world. There are many organisations activity of which is devoted to counteract the light pollution through public education, scientific researches, and co-operation with government administration at all levels - from individual towns and cites to whole states. Owing to this there are many places where laws and regulations have being implemented to reduce the pollution (e.g. Toronto, the State of Connecticut, Slovenia).

